Differences between Single-layer, Double-layer and Multi-layer FPC
Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs) have become an essential component in modern electronics due to their flexibility, lightweight design, and high-density capabilities. Depending on the number of conductive layers, FPCs can be categorized into single-layer, double-layer, and multi-layer types. Each type has its own unique structure, performance characteristics, and ideal applications. This article explores the differences between these three common FPC types and how they are used in various industries.
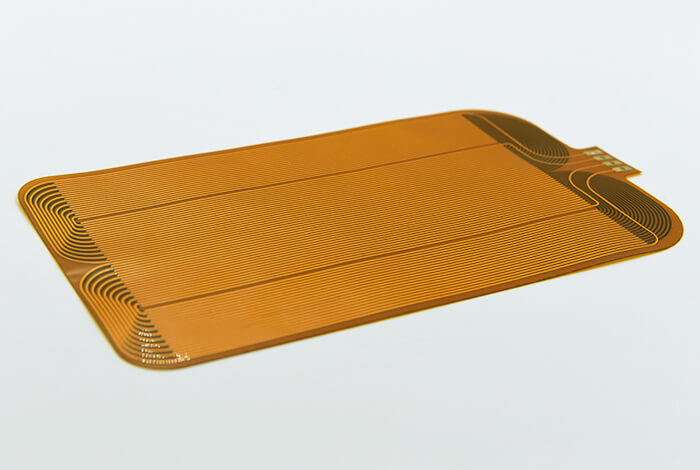
Single-Layer FPC
The simplest form of flexible printed circuit is the single-layer FPC, which consists of a single layer of copper foil bonded to a substrate, typically made of polyimide or PET. A protective coverlay is applied over the copper layer to prevent damage and ensure durability.
Structure:
- Substrate (e.g., polyimide or PET)
- Copper foil with etched circuit pattern
- Coverlay for protection
Features:
- Simple design: The straightforward construction makes it easy to manufacture and cost-effective.
- High flexibility: Ideal for applications that require bending and folding without compromising performance.
- Reliable operation: With fewer components, it offers a lower failure rate and is suitable for basic connections.
Applications:
Single-layer FPCs are commonly used in devices where simple connectivity and flexibility are key, such as printers, scanners, and basic display interfaces.
Double-Layer FPC
A double-layer FPC consists of two copper layers separated by a dielectric substrate. These layers are connected via vias, allowing for more complex circuitry than single-layer designs.
Structure:
- Coverlay
- Top copper layer
- Dielectric substrate
- Bottom copper layer
- Coverlay
Features:
- Enhanced circuit complexity: Allows for circuits to be placed on both sides, increasing functionality.
- Higher circuit density: More wiring and components can be integrated compared to single-layer FPCs.
- Improved reliability: Better suited for applications requiring higher performance and stability.
Applications:
Commonly found in mobile phones, digital cameras, and medical equipment, where moderate complexity and reliability are required.

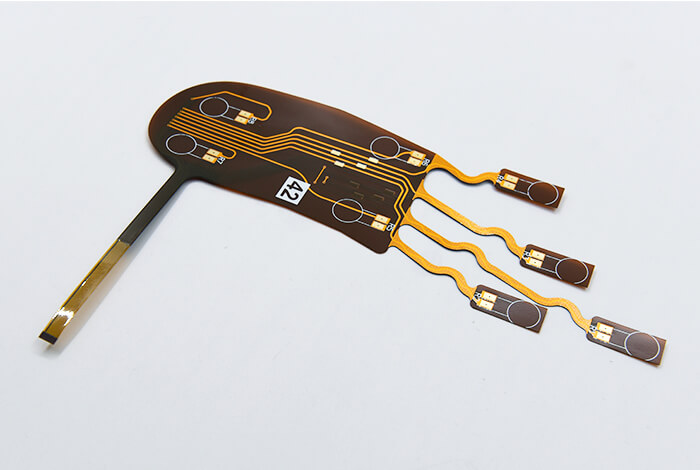
Multi-Layer FPC
Multi-layer FPCs consist of multiple copper layers stacked together and bonded using adhesive layers. Vias connect the different layers, enabling highly complex and compact circuit designs.
Structure:
- Coverlay
- Top copper layer
- Dielectric substrate
- Adhesive + copper layer + substrate (repeated for additional layers)
- Bottom copper layer
- Coverlay
Features:
- High-density design: Supports intricate layouts with multiple signal paths and high component density.
- Greater design flexibility: Circuits can be distributed across multiple layers to optimize space and performance.
- Superior signal integrity: Reduces electromagnetic interference and improves overall signal quality.
Applications:
Used in high-end electronics like smartphones, tablets, aerospace systems, and precision medical devices where advanced performance is critical.
Each FPC type—single-layer, double-layer, and multi-layer—offers distinct advantages depending on the application. Single-layer FPCs are ideal for simple, flexible connections. Double-layer FPCs provide increased complexity and density, while multi-layer FPCs support the most demanding and high-performance applications. Choosing the right type ensures optimal performance, reliability, and efficiency in electronic devices.

Stainless Steel Bar,Hexagonal Bar Steel Rod,Angle Steel Bar,H-Beam Steel
Shandong Rizhaoxin Metal Products Co., Ltd. , https://www.changyisteel.com
